INDEX
Article 1. Objective
Article 2. Output
Article 3. Definitions
Article 4. Scope
Part II - Business on pesticides
Article 5. Business on pesticides
Article 6. Import and export license, selling license
Article 7. Record maintenance
Article 8. Responsibility of pesticide business
Part III - Registration of pesticides
Article 9. Registration of pesticides
Article 10. Exceptions for pesticide registration
Article 11. Qualifications for pesticide registration
Article 12. Application for registration
Article 13. Registration consideration
Article 14. Pesticide registration certificate
Article 15. Withdrawal of pesticide registration certificate
Article 16. Pesticide Registration Unit
Article 17. Formulating pesticides
Article 18. Import-Export of pesticide
Article 19. Distribution or selling of pesticides
Article 20. Transportation
Article 21. Storage
Article 22. Transit
Part V - Use and disposal of pesticides
Article 23. Use of pesticides
Article 24. Disposal of pesticides
Part VI - Packaging Labeling and Advertising
Article 25. Packaging
Article 26. Labeling
Article 27. Advertising
Part VII - Management and inspection
Article 28. Management and inspection of pesticides
Article 29. Inspection of pesticide
Article 30. Types of pesticide inspection
Article 31. Right and duties of Department of Agriculture
Article 32. Right and duties of Provincial Agriculture and Forestry Office (PAFO)
Article 33. Right and duties of District Agriculture and Forestry Office (DAFO)
Article 34. Roles and duties of pesticide inspectors
Part VIII - Fees and Service Charges
Article 35. Fees and Service Charges
Part IX - Rewards and Sanctions
Article 36. Rewards
Article 37. Rewards for government officials
Article 38. Measures towards violators
Article 39. Implementation
Article 40. Effectiveness
Annex 1 - List of banned pesticides in Lao PDR, June 2010
Annex 2 - Different classification of pesticides
Lao People’s Democratic Republic
Peace Independence Democracy Unity Prosperity
Ministry of Agriculture and Forestry No.2860/MAF
Vientiane Capital, dated 11 Jun 2010
Regulation
on the Control of Pesticides in Lao PDR
- Pursuant to the Law on Agriculture No.01/98/NA, dated 6 November 1998;
- Pursuant to the Environment Protection Law No.02/99/NA, dated 3 April 1999;
- Pursuant to Law on Local Administration No.03/NA of 21 October 2003;
- Pursuant to the Law on Food No.04/NA, dated 15 May 2004.
The Minister of Agriculture and Forestry issues the Regulation on the Control of Pesticides as follows:
Article 1. Objective
This regulation defines the principles, rules, and measures for controlling activities that involve pesticides in Lao PDR in order to protect human, animal and plant health, and the environment, and to be harmonized with international obligations and regulations in which Lao PDR is contracting party. Top
Article 2. Output
This regulation is a tool for the monitoring and control of production, processing, import-export, distribution, transportation, storage, use, and proper disposal of pesticides to ensure the safety of people, animals, plants, and the environment. It applies to all stakeholders involved in the use and management of pesticides. Top
Article 3. Definitions
Terms used in this regulation shall be interpreted as follows:
Pesticide means any substances or mixture or substances intended for the prevention, destruction or control of any pest, including vectors of human or animal disease, unwanted species of plants or animals causing harm during or otherwise interfering with the production, processing, storage, transport or marketing of food, agricultural commodities, wood and wood products or animal feedstuffs, or substances which may be administered to animals for the control of insects, arachnids or other pests in or on their bodies. The term includes substances intended for use as a plant growth regulator, defoliant, desiccant or agent for thinning fruit or preventing the premature fall or fruit, and substances applied to crops either at pre-or post harvest to protect the commodity from deterioration during storage and transport.
Banned pesticide means a pesticide for which all uses have been prohibited by final regulatory action, in order to protect human health or the environment. The term includes a pesticide that has been refused approval for first-time use, or had been withdrawn by industry either from the domestic market or from further consideration in the domestic approval process, and where there is clear evidence that such action has been taken in order to protect human health or the environment.
Unwanted plant means any plant that is not grown intended and is considered undesirable.
Pesticide industry means all those organizations and individuals engaged in manufacturing, formulating or marketing pesticides and pesticide products.
Trader means anyone engaged in trade, including export, import and domestic distribution.
Formulation means the combination of various ingredients designed to render the product useful and effective for the purpose claimed; the form of the pesticide as purchased by users.
Active ingredient means the biologically active part of the pesticide.
Registration means the process whereby the responsible national government or regional authority approves the sale and use of a pesticide following the evaluation of comprehensive scientific data demonstrating that the product is effective for the intended purposes and does not pose an unacceptable risk to human or animal health or the environment.
Label means the written, printed or graphic mater on, or attached to, the pesticide or the immediate container thereof and also to the outside container or wrapper of the retail package of the pesticide.
Manufacturer means a corporation or other entity in the public or private sector or any individual engaged in the business or function (whether directly or through an agent or entity controlled by or under contract with it) of manufacturing a pesticide active ingredient or preparing its formulation or product.
Distribution means the process by which pesticides are supplied through trade channels to local or international markets.
Advertising means the promotion of the sale and use of pesticides by printed and electronic media, signs, displays, gift, demonstration or word of mouth.
Personal protective equipment means any clothes, materials or devices that provide protection from pesticide exposure during handling and application.
Disposal means any operation to recycle, neutralize, destroy or isolate pesticide waste, used containers and contaminated materials.
Residue means any specified substances in or on food, agricultural commodities or animal feed resulting from the use of a pesticide. The term includes any derivatives of a pesticide, such as conversion products, metabolites, reaction products and impurities considered to be of toxicological significance. The term ‘‘pesticide residue’’ includes residues from unknown or unavoidable sources (e.g. environmental) as well as known uses of the chemical.
Risk is function of the probability of an adverse health or environmental effect, and the severity of that effect, following exposure to a pesticide.
Toxicity means a physiological or biological property which determines the capacity of a chemical to do harm or produce injury to a living organism by other than mechanical means.
Integrated Pest Management (IPM) means the careful consideration of all available pest control techniques and subsequent integration of appropriate measures that discourage the development of pest populations and keep pesticides and other interventions to levels that are economically justified and reduce or minimize risks to human health and the environment. IPM emphasizes the growth of a healthy crop with the least possible disruption to agro-ecosystems and encourages natural pest control mechanisms.
Natural enemies mean beneficial diseases or insects, such as predators, parasitoids, and pathogens, which can play a role in natural pest control. Top
Article 4. Scope
This regulation applies to all persons, juristic persons or organizations engaged in manufacturing, importing, exporting, selling, using, transporting, storing, destroying and disposing pesticides in Lao PDR. Top
Part II
Business on pesticides
Article 5. Business on pesticides
A person, juristic or organization having the intention to conduct business involving pesticides shall require a license from Agriculture sector and other related sector for approval and shall register the enterprise with industry and commerce sector as determined by the Law on Enterprises. Top
Article 6. Import and export license, selling license
Any person, juristic or organization intending to import or export registered pesticides shall apply for a license from the Ministry of Agriculture or its provincial representatives at least 3 working days prior to import or export and 20 days prior to sale of pesticides. Top
Article 7. Record maintenance
A person, juristic person or organization involved in import, export, manufacture or storage of pesticides shall maintain records and other information needed for monitoring the management of these pesticides. Top
Article 8. Responsibility of pesticide business
A person conducting pesticide business shall ensure risks to human health, animal health and the environment are minimized. In the event of an accident whereby pesticides cause damage to humans, animals or the environment, the pesticide business operator shall be punished by applicable laws.
The pesticide business operators shall cooperate with pesticide inspectors and other relevant authorities to facilitate corrective action. Top
Part III
Registration of pesticides
Article 9. Registration of pesticides
All pesticides produced, imported, exported, distributed and used in Lao PDR must be registered with the Department of Agriculture, Ministry of Agriculture and Forestry. Top
Article 10. Exceptions for pesticide registration
- Registration is not required for botanical pesticides that are not packed for sale; and
- After inspection by Ministry of Agriculture and Forestry, provisional registration can be granted for products imported for the purpose of research, trial or exhibition, if evidence is provided that the products are registered in the country of origin. Top
Article 11. Qualifications for pesticide registration
Any person, juristic person or organization eligible to register pesticide shall have the following qualifications:
- Person holding a license as described in Article 19 of this regulation; and
- Imported pesticide shall be registered in exporting country. Top
Article 12. Application for registration
The registration application shall comprise the following documents:
- Copy of enterprise registration certificate;
- Copy of pesticide registration certificate of exporting country or/and country of origin;
- Nomination letter for registration from manufacturer or exporting country;
- Use instructions for the pesticide concerned; and
- A sample of the pesticide. Top
Article 13. Registration consideration
Department of Agriculture shall review the request and decide to approve or reject registration within 60 days from the date the application is received. In the case of rejection, written notice shall be given to the applicant by the DOA. Top
Article 14. Pesticide registration certificate
A pesticide registration certificate is an official document issued by the Director General of DOA, Ministry of Agriculture and Forestry and remains valid for two years. Two months prior to expiration, the owner shall submit a request for renewal of the certificate to the DOA. The application and process of consideration will proceed as described in article 12 and 13 of this regulation. Top
Article 15. Withdrawal of pesticide registration certificate
The pesticide registration certificate may be withdraw prior to its expiration date by the Director General of Department of Agriculture in any of the following cases:
- There is a serious violation of this regulation or other related laws by the certificate holder or their authorized representatives;
- The pesticide is no longer effective for its intended use; or
- The pesticide has been withdrawn from the market.
In case of cancellation of a registration, the Department of Agriculture shall fix a reasonable phasing-out period for the distribution and use of the product concerned. Withdrawal of a certificate of registration shall be communicated to all relevant agencies. Top
Article 16. Pesticide Registration Unit
The Pesticide Registration Unit is a unit under the administration of the Department of Agriculture, Ministry of Agriculture and Forestry, which has the following main roles and duties:
- Review applications for the registration of pesticides and take registration decisions:
- Regularly review the list of registered pesticide to determine whether these still meet the requirements, taking into consideration the latest scientific information;
- Edit and approve labels of pesticides; and
- Implement others rights and task as described in related legislations. Top
Part IV
Management of production, import, export, distribution, transportation, storage and transit of pesticides
Article 17. Formulating pesticides
A person, juristic person or organization having the intention to formulate pesticides shall submit an application to the Ministry of Agriculture and Forestry, which should include a report of a feasibility study and a description of the techniques to be used. Top
Article 18. Import-Export of pesticide
Only registered pesticides can be imported or exported. Registration has to be obtained from the Department of Agriculture, Ministry of Agriculture and Forestry. Import and export shall comply with other related laws. This does not apply to pesticides determined in Article 10 of this regulation. Top
Article 19. Distribution or selling of pesticides
Distributors or traders must meet the following criteria:
- They should have attended a training course on pesticide management and hold a related certificate;
- They should possess safety instructions for the handling and use of pesticides to ensure that they are not causing negative effects to people and the environment;
- They should supply protective clothing to customers;
- Storage must strictly meet the requirements in article 21 of this regulation;
- They must maintain records of sales and purchase orders.
Distributors or traders of pesticides are prohibited to:
- Distribute pesticides without the necessary licenses obtained from the concerned authorities;
- Sells pesticides that
- are not registered in Lao PDR
- exceeded their expiry date, have deteriorated (changed physical appearance or initial formulation, such as color, sedimentation, solubility) or have a broken or leaking container;
- lack a label or have a damaged or otherwise not readable label; or
- have been repacked for sale in inappropriate packaging. Top
Article 20. Transportation
Transporters carriers of pesticide shall adhere to the following rules:
- For consignment of pesticides, either of same or different products, exceeding 1,000 liters (liquids) or 1,000 kg (solids), separate documentation has to be issued and be kept with the driver. The documentation shall have the following contents:
- Name, address and phone number of owner and shipper
- Trade name or common name of transported pesticide
- Formulation types and concentrations of pesticides transported
- Volume of pesticides
- Emergency procedures in the case of breakage or spill
- A safety data sheet for each of the products transported.
- For consignments greater than 1,000 liters or 1,000 kg the transport route must be declared in advance;
- Pesticides carried by means of public transport shall not exceed 20 liters for liquids or 20 kg for solids. Products shall be packed properly and kept separately from the passengers and other goods;
- The drivers of vehicles carrying pesticides shall be selected properly and shall be reliable and competent; and
- Transportation of pesticides together with living organism and others goods is prohibited. Top
Article 21. Storage
If pesticides are stored in amounts of more than 10 liters or kilograms, the following requirements should be met:
- A pesticide storage facilities should be located in an area where flooding in unlikely and at least 100m distance from housing and domestic animal farm;
- All pesticides must be kept in a facility that can be locked and labeled as a pesticide storage area;
- Pesticides must be kept away from heat or direct sum exposure;
- Pesticides should be separated from other goods;
- Pesticides must be stored by group of hazard classification;
- Pesticides should be kept in their original containers with label;
- Absorbent substances such as charcoal, sawdust or sand should be available;
- Storage floors should be kept clean and dry, and cleaned up if spillage or leaking of pesticides occurs;
- Soap and water should be available for washing in case of contact with a pesticide;
- Use stands or pallets for placing of pesticides in order to avoid direct contact with the floor;
- Keep empty containers in a safe place prior to disposal. Top
Article 22. Transit
All pesticides passing in transit through Lao PDR shall comply with relevant bilateral or multilateral agreements to which Lao PDR is a party. Top
Part V
Use and disposal of pesticides
Article 23. Use of pesticides
Any person intending to use a pesticide shall recognize its characteristics and pay attention to following matters:
- Use Integrated Pest Management and give priority to controlling pests by using natural enemies;
- Use pesticide properly and as described on the label;
- Wear protective equipment whenever applying pesticides. Employers should provide employees with proper equipment and training in pesticide application;
- Ensure that the necessary measures are taken to prevent harmful effects of pesticides to human health, animals and the environment; and
- Any accident involving pesticides that requires specialist assistance or poses a threat to human health or the environment should immediately be reported to the relevant authority. Top
Article 24. Disposal of pesticides
Substandard or counterfeit pesticides, expired products or pesticide waste, including empty containers shall be properly disposed or buried in an approved landfill without risk to environment. The location should be on a flat ground, far from water resources, well or ground water and follow the technical guidelines specified by Water Resources and Environment Administration (WREA). Top
Part VI
Packaging Labeling and Advertising
Article 25. Packaging
Repacking of pesticides is prohibited unless specific permission has been obtained from the Pesticide Registration Unit, DOA. Pesticides should be kept in their original packaging during the importation, transportation, storage and distribution in order to prevent harmful effects to human and/or animal and the environment. Top
Article 26. Labeling
All packaging of pesticides should have affixed labels on the pesticide container. The label must be in Lao and/or English language and be easy to read. It should not tear easily.
-
The contents and form of label shall be approved by the Pesticide Registration Unit, and contain the following information:
1.1. Trade name;
1.2. Chemical (common) name, formulation and concentration of active ingredient(s);
1.3. Purpose of usage, e.g. which crops and pests;
1.4. Dosage and mode of application;
1.5. Signs and instructions as described in paragraph 2 of this article;
1.6. Directions for storage, mixing, usage, packaging and recommended personal protection from hazards;
1.7. Withholding period;
1.8. Warnings;
1.9. Symptoms of poisoning, antidote, directions for physician;
1.10. Hazard classification;
1.11. Name of producer;
1.12. Volume of package;
1.13. Production or expiry date; and
1.14. License number. -
Instructions for labeling:
2.1. Pesticide under WHO hazard Class Ia must be labeled with a clear danger sign, the skull and crossed bones, and bear the text ‘extremely toxic’ which should be accompanied by the appropriate signs on red stripe as under 3 below;
2.2. Pesticide under WHO hazard Class Ib must be labeled with a clear danger sign, the skull and crossed bones, and bear the text ‘highly toxic’, accompanied by the appropriate signs on yellow stripe as under 3 below;
2.3. Pesticide under WHO hazard Class II must be labeled with a clear danger sign, flash, and bear the text: ‘dangerous’, accompanied by the appropriate signs on blue stripe as under 3 below;
2.4. Pesticide under WHO hazard Class III must bear the text ‘caution’ accompanied by the appropriate signs as under 3 below. -
The following symbols and phrases shall be used to mark the precaution measures:
3.1.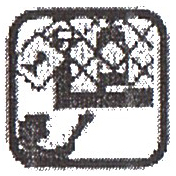 Keep away from children;
Keep away from children;
3.2. Wash after handling;
Wash after handling;
3.3. Dangerous to animals;
Dangerous to animals;
3.4. Dangerous to fish and aquatic animals, prohibited to contaminate water resource;
Dangerous to fish and aquatic animals, prohibited to contaminate water resource;
3.5. The following phrases shall be used in either ‘‘usage’’ or ‘‘mixing’’ directions as appropriate:
3.5.1.  Wear eye protection;
Wear eye protection;
3.5.2.  Wear breathing protection;
Wear breathing protection;
3.5.3.  Wear mask;
Wear mask;
3.5.4. 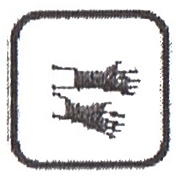 Wear gloves;
Wear gloves;
3.5.5.  Wear protective clothing during spraying or handling;
Wear protective clothing during spraying or handling;
3.5.6. 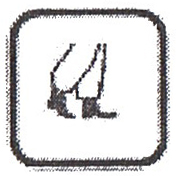 Wear rubber boots. Top
Wear rubber boots. Top
Article 27. Advertising
A person, juristic person or organization shall only advertise registered pesticides. False statements or exaggerations that may lead to misunderstanding among users are prohibited. Top
Part VII
Management and inspection
Article 28. Management and inspection of pesticides
Pesticide management and inspection sections comprises of:
- Department of Agriculture, Ministry of Agriculture and Forestry;
- Provincial Agriculture and Forestry Office;
- District of Agriculture and Forestry Office.
These three sections will assign staff to a pesticide inspection unit which will include trained staff on pesticide management from DOA. Top
Article 29. Inspection of pesticide
Inspection of pesticides refers to monitoring of pesticide manufacturing process, import-export , sale, distribution, advertising, storage, use of pesticides, and disposal of expired pesticide or pesticide waste including empty containers for compliance with laws of Lao PDR. This is also applies to individual farms, concession farms, government and private farms. Top
Article 30. Types of pesticide inspection
There are three types of pesticide inspections:
- Regular inspection;
- Inspection with advance notice; and
- Immediate inspection.
Regular inspection refers to an inspection performed regularly according to plan at pre-determined times which shall be conducted at least once a year.
Inspection by advance notice refers to an inspection which is not included in the plan, which is performed when deemed necessary and for which advance notice is given.
Immediate inspection refers to a sudden inspection performed without advance notice to the person to be inspected. Top
Article 31. Right and duties of Department of Agriculture
The Department of Agriculture has following rights and duties regarding the management and inspection of pesticides:
- To conduct research on policies, laws and regulations on management and inspection of pesticides and make proposals to the Minister for consideration;
- To disseminate policy, laws and regulations on pesticide management and inspection, and provide training;
- To cooperate with related agencies and local administration for pesticide management and inspection;
- To implement the pesticide registration scheme as specified in PART III and make available regular updated of the lists of registered and banned pesticides;
- To monitor the validity of licenses for the import-export of pesticides;
- To train and upgrade officials involved in pesticide management and inspection on political, ideological, moral, and technical aspects;
- To appoint inspectors and to provide them with the necessary badge to empower them to conduct their task;
- To provide training to traders for obtaining basic knowledge about pesticides and their risks;
- To cooperate with international organizations on pesticide management and inspection;
- To regularly report to government on the implementation of its duties on pesticide management and inspection throughout the country;
- To exercise other rights and duties as stipulated in related legislations. Top
Article 32. Right and duties of Provincial Agriculture and Forestry Office (PAFO)
Provincial Agriculture and Forestry Office have following rights and duties regarding the management and inspection of pesticides:
- To supervise the implementation of laws and regulations on pesticide management and inspection within its own province;
- To issue import licenses to persons or juristic persons who request such licenses and meet the requirements. Pesticides to be imported should be registered and quantities should be in line with use requirements of the local province to avoid over-supply and products being stored beyond their expiry date;
- To issue sale and/or import licenses to persons or juristic persons who meet the requirements for such business;
- To conduct inspection of pesticide shops in their provinces and to follow up on cases of violation;
- To make available the necessary staff and budget to fulfill the duties assigned under this regulation;
- To propose staff to serve as provincial pesticide inspectors for approval by the Minister of Agriculture and Forestry;
- To cooperate with other agencies involved in pesticide management and inspection;
- To regularly report to the Ministry of Agriculture and Forestry on the implementation of its duties in pesticide management and inspection; and
- To exercise other rights and duties as stipulated in related legislations. Top
Article 33. Right and duties of District Agriculture and Forestry Office (DAFO)
Right and duties of District Agriculture and Forestry Office have the following rights and duties:
- To implement the laws and regulations on pesticide management and inspection within its responsible area;
- To cooperate with other agencies involved in pesticide management and inspection;
- To regularly report to PAFO on the implementation of its duties in pesticide management and inspection; and
- To exercise other rights and duties as stipulated in related legislations. Top
Article 34. Roles and duties of pesticide inspectors
Pesticide inspectors have the following roles and duties:
- Inform all stakeholders concerned with pesticides of this regulation;
- The inspectors shall present their identity card and the authorization to the person to be inspected every time and should strictly follow this regulation;
- Carry out periodic inspections of all persons or organizations involved in import-export, manufacturing, packing or repacking, labeling, storing, selling, distributing, advertising or using pesticides for adherence to this regulation;
- Carry out regular checking of the products, trading patents, pesticides licenses and records as well as other documentation or authorization granted or issued under this regulation;
- Collect samples of any pesticide, substances or other objects related to pesticide for analysis;
- Seize any equipment, pesticide, document, record, or other item which the Inspector believes has been used in, or which appears to afford evidence of, a violation of this regulation, as long as:
- The inspector hands over a receipt in the prescribed form to the person from whose custody the item was taken;
- the item is returned to the person once the inquiry has been completed, except for illegal pesticides, which if so declared by the court, shall be disposed as prescribed in article 24 of this regulation;
- Take the appropriate action with the responsible authorities to follow up on violation;
- Prepare the report of violation that required fining to the PAFO and DG of DOA. Top
Part VIII
Fees and Service Charges
Article 35. Fees and Service Charges
Fees and service charges for pesticide registration certificates or licenses shall be based on a circular of the Ministry of Finance on fees and service charges which are promulgated from time to time. Top
Article 36. Rewards
Any person, juristic person or organization performing well in implementing this regulation shall be adequately rewarded and appropriately recognize as determined by Ministry of Agriculture and Forestry. Top
Article 37. Rewards for government officials
Government official involved with pesticides continuously over 5 years shall receive an early retirement pension as described in article 59 of the Labor Law. Top
Article 38. Measures towards violators
Any person, juristic person or organization having violated this regulation shall be educated, warned, fined or punished, depending on the severity of the case, as follows:
1st violation: educate, warn and record in file;
2nd violation: seize goods and fine 50 percent of the good’s value according to the market price and record in the file;
3rd violation: seize goods and fine twice of the good’s value according to the market price, record in the file, collaborate and submit to the concerned authority for temporary closure or full closure of the business depending on case severity.
Any violation, first, second or third, that causes severe consequences to the environment or human, animal or plant health, shall be punished according to criminal law. Any person, who suffers damage caused by the import-export, manufacture, packaging or storage of pesticides which are unqualified and dangerous to human health or environment, or results from illegal action, shall be compensated by the competent court. In case of such violation, disposal or returning the pesticides to the exporting country, all expenditure shall be borne by the violator. Top
Article 39. Implementation
The Department of Agriculture, Ministry of Agriculture and Forestry, in collaboration with other concerned organizations shall implement this regulation effectively. Top
Article 40. Effectiveness
This regulation is effective from the date of signature by Minister of Agriculture and Forestry. Any decrees, regulations or provisions contradicted to this regulation are repealed. Top
Minister of Agriculture and Forestry
Sitaheng RASAPHONH
Annex 1 - List of banned pesticides in Lao PDR, June 2010
Insecticides and acaricides
1. Aldrin
2. BHC
3. Chlordane
4. Chlordimeform
5. Chlorfenvinphos
6. Chlorthiophos
7. Cyhexatine
8. DDT
9. Dieldrin
10. Dimefox
11. Dinitrocresol
12. Demeton
13. Endrin
14. Endosulfan
15. Ethyl Parathyon
16. EPN
17. Heptachlor
18. Hexachloro cyclohexane
19. Leptophos
20. Lindane
21. Methamidophos
22. Methomyl
23. Methyl parathion
24. Monocrotophos
25. Polychlorocamphene
26. Phorate
27. Schradan
28. TEPP
29. Toxaphene
Fungicides
30. Binapacryl
31. Captafol
32. Cycloheximide
33. Mercury and mercury compounds
34. MEMC
35. PMA
36. Selenium compound
Rodenticides
37. Chlorobenzilate
38. Sodium fluoroacetate
Herbicides
39. 2, 4, 5 –T
40. Dinoseb
41. Dinoterb acetate
42. Paraquat
43. Sodium chlorate
Fumigants
44. EDB
45. Ethylene oxide
46. Methyl bromide
Others
47. Arsenic compound
48. Calcium arsenate – herbicide, rodenticide, molluscicide, insecticide
49. DBCP – Nematocidide
50. Daminozide – Plant growth regulators
51. Fluoroacetamide – Insecticide, rodenticide
52. Oxamyl – Insecticide, acaricide, termiticide
53. Phosphamidon – Insecticide, nematodicide
54. Sodium Arsenite – Insecticide, fungicide, herbicide, rodenticide
55. Thallium (i) sulfate – Rodenticide, insecticide. Top
Annex 2 – Different classification of pesticides
I. Classification of pesticides based on their purpose
1. Algicides
2. Antifouling agents
3. Antimicrobials and biocides
4. Attractants
5. Biopesticides
6. Disinfectants and sanitizers
7. Fungicides
8. Fumigants
9. Herbicides
10. Insecticides
11. Miticides (also called acaricides)
12. Microbial pesticides
13. Molluscicides
14. Nematicides
15. Ovicides
16. Pheromones
17. Repellents
18. Rodenticides
The term pesticide also includes:
1. Defoliants
2. Desiccants
3. Insect growth regulators
4. Plant growth regulators
II. Classification of pesticides by hazard
1. WHO defines the following hazard classes:
Ia – Extremely toxicity
Ib – Highly hazardous
II – Moderately hazardous
III – Slightly hazardous
U – Unlikely to present acute hazard
2. Classification of pesticide by hazard:
2.1. Chemical substances or pesticides chemicals which are classified should refer to The WHO Recommended Classification of Pesticides by Hazard and Guideline to Classification.
2.2. Any products which not belong to 2.1 should follow the particular regulation
3. The classification of pesticides by hazard shown in 2.1 refer to the Formulated Product or Finished Product are defined by Lethal Doses (LD50) present in this table:
|
WHO Class |
LD50 for the rat (mg/kg body weight) |
||
|
|
|
Oral |
Dermal |
|
Ia |
Extremely hazardous |
- < 5 |
< 50 |
|
Ib |
Highly hazardous |
5 - 50 |
50 - 200 |
|
II |
Moderately hazardous |
50 - 2000 |
200 - 2000 |
|
III |
Slightly hazardous |
> 2000 |
> 2000 |
|
U |
Unlikely to present acute hazard |
5000 or higher |
|
|
LD50 (Lethal Doses) value is statistical estimate of the number of mg of toxicant per kg of body weight required to kill 50% of a large population of test animals; the smaller the LD50 value indicates higher acute toxic. Mg – mass of toxic substance Kg – body weight of live animal |
| # | Title | Download |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | Regulation on Control of Pesticides in Lao PDR No. 2860/MAF |  PDF PDF |
| 2 | ຂໍ້ຕົກລົງ ວ່າດ້ວຍ ການຄຸ້ມຄອງ ຢາປາບສັດຕູພືດ ໃນ ສປປ ລາວ ເລກທີ 2860/ກປ |  PDF PDF |
Please share your feedback below and help us improve our content.
